|
The
utilization of abrasive waterjet
(AWJ) cutting/drilling, and in
particular its application into
hard-to-cut materials, is growing.
However, the mechanics of AWJ
cutting is complex; the material
removal process is not fully
understood and, consequently, it has
not been accurately modeled. In the
current study, work was undertaken
to mesh in a first stage the
waterflow into the waterjet nozzle
in order to use the finite element
(FE) method to simulate the pure
waterjet flow. The main objective is
to investigate and analyze in detail
the workpiece material behavior
under waterjet impingement; a
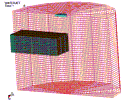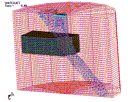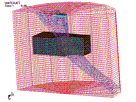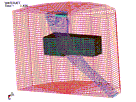
non-linear FE model (using LS-DYNA
3D code) has been developed, which
simulates the erosion of the target
material caused by the high-pressure
waterjet flow. A combination of
Eulerian–Langrangian elements is
used for the waterjet and the target
material, respectively, in order to
handle their interaction. Damaged
zones can be localized on impinged
materials. Elements’ failure is
handled by introducing a threshold
strain after which Langrangian
elements are removed. The results
obtained from this numerical
simulation (velocity profile,
stress, erosion stages) show a good
agreement with the results from
previous experimental work that is
available in bibliography. |
 |